Internet Basics: Getting Started on the Web
NOTE: All screenshots featured in this class are from the Google Chrome internet browser.
I. About the Internet
A. What is the Internet or Web?
Definitions
- Internet—a network made up of computers all over the world, connected electronically by telephone lines, fiber-optic cables, and other links. It is a "network of networks." Note that no single organization owns or controls the Internet.
- Wi-Fi—allows computers, smartphones, or other devices to connect to the Internet or communicate with one another wirelessly within a particular area.
- Web or World Wide Web—the part of the Internet that uses text, images, sound and video. It is huge and growing every day.
B. What can I do on the Internet?
- Search for and access information
- Use email
- Access social media
- Search for jobs
- Shop for goods and services
C. What information can I find on the web?
Countless subjects and topics can be found on the web, but not everything on the Internet is true. Always remember that anyone can publish something on the web: information may not be accurate and sites may be offensive to some. Not everything is free and always look for a “secure site” notification when your order something on the Internet.
D. Web Browsers
A web browser is a software program that allows you to see and read the information on the World Wide Web. Some popular examples of a web browser are:
 Google Chrome—This is the browser used most by library staff, because it is faster, more secure, and more user friendly than some other internet browsers available.
Google Chrome—This is the browser used most by library staff, because it is faster, more secure, and more user friendly than some other internet browsers available.
 Mozilla Firefox—Another internet browser that is user friendly and includes some security features; but it does require a lot of memory to operate efficiently, which may limit the computer’s ability to do multiple tasks simultaneously.
Mozilla Firefox—Another internet browser that is user friendly and includes some security features; but it does require a lot of memory to operate efficiently, which may limit the computer’s ability to do multiple tasks simultaneously.
 Microsoft Internet Explorer—Before Google Chrome and Mozilla Firefox, there was Internet Explorer. The first of its kind, it allowed people to browse the internet, listen to music, shop online, etc., and it still does; however, Google Chrome and Mozilla Firefox are faster, more user friendly, and more secure than Internet Explorer.
Microsoft Internet Explorer—Before Google Chrome and Mozilla Firefox, there was Internet Explorer. The first of its kind, it allowed people to browse the internet, listen to music, shop online, etc., and it still does; however, Google Chrome and Mozilla Firefox are faster, more user friendly, and more secure than Internet Explorer.
E. Internet Service Providers
An Internet Service Provider (or ISP) is the company you pay to gain access to the Internet through your computer. They will give you a browser to use. Two common ISPs in Henrico are Comcast and Verizon.
F. Home Page
A home page can be one of two things:
- The introductory or first page of a Web site.
- The page set to load when opening your internet browser. You can customize this to whatever page you choose.
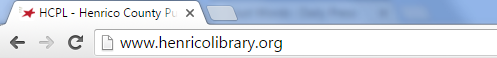
G. Address Bar
The address bar is a text box in a web browser displaying the address of the web page that is currently being viewed.
II. Navigation
A. Scrolling
Scrolling allows you to move up and down and side to side on a webpage. You may use the mouse or the arrow keys on the keyboard.
- Identify your horizontal and vertical scroll bars and briefly practice scrolling.
B. Links
Links allow you a way to move from one site and/or page to another site and/or page. There are two types of links:
Text links are parts of the web page text that are generally in a different color, and often underlined. The mouse pointer will turn into a hand when it moves over a link.
- Place your mouse pointer over this text link.
- When you see the hand, click once.
Graphic links are graphics or pictures that will also show a hand when the mouse pointer moves over them.
C. Back/Forward buttons

The back and forward buttons allow you to move backward and forward between sites you have already visited.
- Click on the Back button, and then the Forward button to return here.
D. Home button

The home button takes you to the page that is set to load when first opening the browser. On library computers, the home button is set to the library home page.
E. Refresh button

Pages can sometimes take too long to load or get stuck. When this happens, you can click on the stop button to end the search. This is sometimes needed during peak times of usage.
III. Web Addresses
Each web site has a unique address, just like we have a unique Social Security number. This allows us to locate a site quickly. This address is also called a URL (Universal or Uniform Resource Locator). Example: http://www.henricolibrary.org.
A. Parts of a URL
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 5 | |
| 4 | ||||
| https:// | www. | henricolibrary | .org | /events |
- Protocol—http:// stands for HyperText Transfer Protocol; https:// stands for HyperText Transfer Protocol Secure. It’s not really important to know what those mean, but most web site addresses start with one or the other.
- Host name—www stands for world wide web. It is the name of the specific computer you are contacting.
- Domain name—The main part of the address (ex: cnn.com or henricolibrary.org) is the specific web site name. Often it is the name of the company or organization, or some variation of it.
- Top-level domain—The last part of the domain name often indicates the type of organization that runs the site. Below are some common examples of address endings that are used today:
- .com – commercial organization
- .gov – US government agency
- .mil – US military
- .edu – educational institution
- .org – nonprofit organization
- .net – network provider
- .uk, .ca, .fr, etc. – sites based in other countries (United Kingdom, Canada, France, etc.)
- Directories—Slashes after the main address represent subsections or specific pages within the web site. Example: www.henricolibrary.org/events will take you to the Featured Events listings on the library's site.
B. How to type in a web address and connect to a site
You have to type the address exactly, paying attention to upper and lower cases, slashes and dots. Most browsers will put the http:// in for you. Some may even put in the www for you.
Let’s practice.
- First, open a new tab. Then click in the address box and begin typing a website address from the table below.
| www.nbc12.com | www.royal.gov.uk | www.richmond.edu |
| www.fbcrichmond.org | www.virginia.gov | www.vmfa.museum |
| www.slideshare.net | www.usmc.mil | www.richmond.com |
| Nike | amazon | www.pbs.org |
- When you are finished, please return to this class web page.
IV. Bookmarks
A bookmark is a saved shortcut that directs your browser to a specific webpage. It stores the title and web address of the corresponding page. Saving bookmarks allows you to easily access your favorite locations on the Web.
To bookmark a website, do the following:
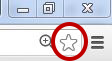
- In Google Chrome, find the star symbol at the right end of the address bar and click on it.
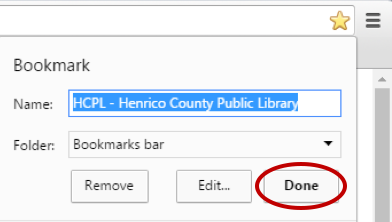
- After you’ve clicked on the star symbol, a small box will appear. Here you can edit the name of the bookmark. When you are finished, click “Done”.
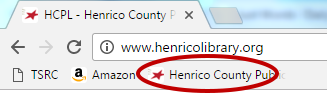
- The website will be added to the Bookmarks bar, which is located under the address bar in your Internet browser. You can now click on that shortcut instead of typing in the entire web address.
V. Search Engines
Search engines are programs that search databases of web documents matching key words supplied by the user.
Several examples of search engines include Google, Bing, Ask.com, and Yahoo.
- Click on this link: https://www.google.com/
- In the text box, type "boxer dog" (include the quotes), then either press the Enter key or click on the Google Search button.
- A list of sites will appear. Notice the total number of results (or hits) that were found.
- Click on one of the listed sites.
There are numerous other search engines available. Here are links to some others:
VI. Time to Play
Pick from the following topics and search for websites related to that topic:
| Recipes | White Pages | Travel |
| Sports | Shopping | Weather |
VII. Evaluation of Web Resources
Remember, anyone can publish on the web. It is important to evaluate the information you find. What should you look for?
- Look at the "About" or "About Us" part of the website. This can tell you who is behind the website, and if they are an authority on the subject. You may also be able to tell if they have an ulterior motive or biased point of view.
- Look for a date. This lets you know when the page was last updated. Beware of websites which are not being well-maintained with current information.
- A tilde (~) symbol in a long address usually represents an individual's own web site.
- Beware of trusting sites with misspelled words, factual errors, or typos.
VIII. Error/Security Messages
Here are some of the most common reasons for an error or security message. These can come from several different things, which include:
- When typing in an address, a typo could have been made.
- The computer you are trying to contact may be temporarily busy or down.
- The address may be out-of-date or incorrect. Web addresses can and often do change.
Sometimes there is no way to know precisely what is causing the error message. Clicking on the back button will get you out of the error message in most cases.
IX. Internet Safety
Stay safe …
- Create stronger passwords. Create passwords that are unique and hard to guess, and don’t share them with others. Including numbers, acronyms, and special characters makes them extra secure.
- Don’t expose personal information. Be aware of how much of your personal or financial data you might be sharing with strangers on social networking sites, through e-mail, and on special-interest sites.
- Always log out properly. When using a public computer, be sure to log out of any accounts that you may have had open (email, banking, etc.). Remember, simply closing your browser (clicking the red ‘x’) does not mean that you are logged out!
- Don’t fall for e-mail scams. Online criminals may use e-mail to get your personal information and steal your identity. Or an e-mail might entice you to click a link that takes you to a bogus site or downloads malware (malicious software) to your computer.
- Know who you’re doing business with. It’s quick and easy to create a Web site that looks legit, but not all Web sites are.
- Be cautious with e-mail attachments. Attached files may contain malware, which can damage your computer — or it may install code that can track your activities.
- Install security software. Make sure the computer has security software on it and also check that the auto-update feature is enabled to ensure your computer has the latest security.
- Look for the padlock. When shopping or banking online, always look for the padlock icon in your Internet browser as well as https:// before the rest of the web address. This lets you know that the website is secure.

Social Media
What is social media?
Social media includes websites and applications that enable users to create and share content.
What is a social network?
A social network is a dedicated website or other application that enables users to communicate with each other by posting information, comments, messages, images, etc. Examples of social networks include Facebook and Twitter.
Facebook is a website where you can create a personal profile, contact people that you know, and keep in touch by sharing information such as updates on your activities, pictures and other interests.To sign up for a Facebook account, visit www.facebook.com.
Twitter is a real-time information network that connects you to the latest information about what you find interesting. Simply find the public streams that you find most compelling and follow the conversations. The public stream is the millions of posts written by ordinary people, organizations, news outlets and celebrities every day. To sign up for a Twitter account, visit www.twitter.com.
X. Further Questions
The best way to continue learning how to use the Web is to PRACTICE, PRACTICE, PRACTICE! Some online sources for continued learning:
- TechBoomers—A free educational website where inexperienced Internet users with basic computer skills can learn about popular and trusted websites. https://techboomers.com
- GCF—The Goodwill Community Foundation has free tutorials for all kinds of topics, including using the internet. https://www.gcflearnfree.org
Revised 2/23/18
